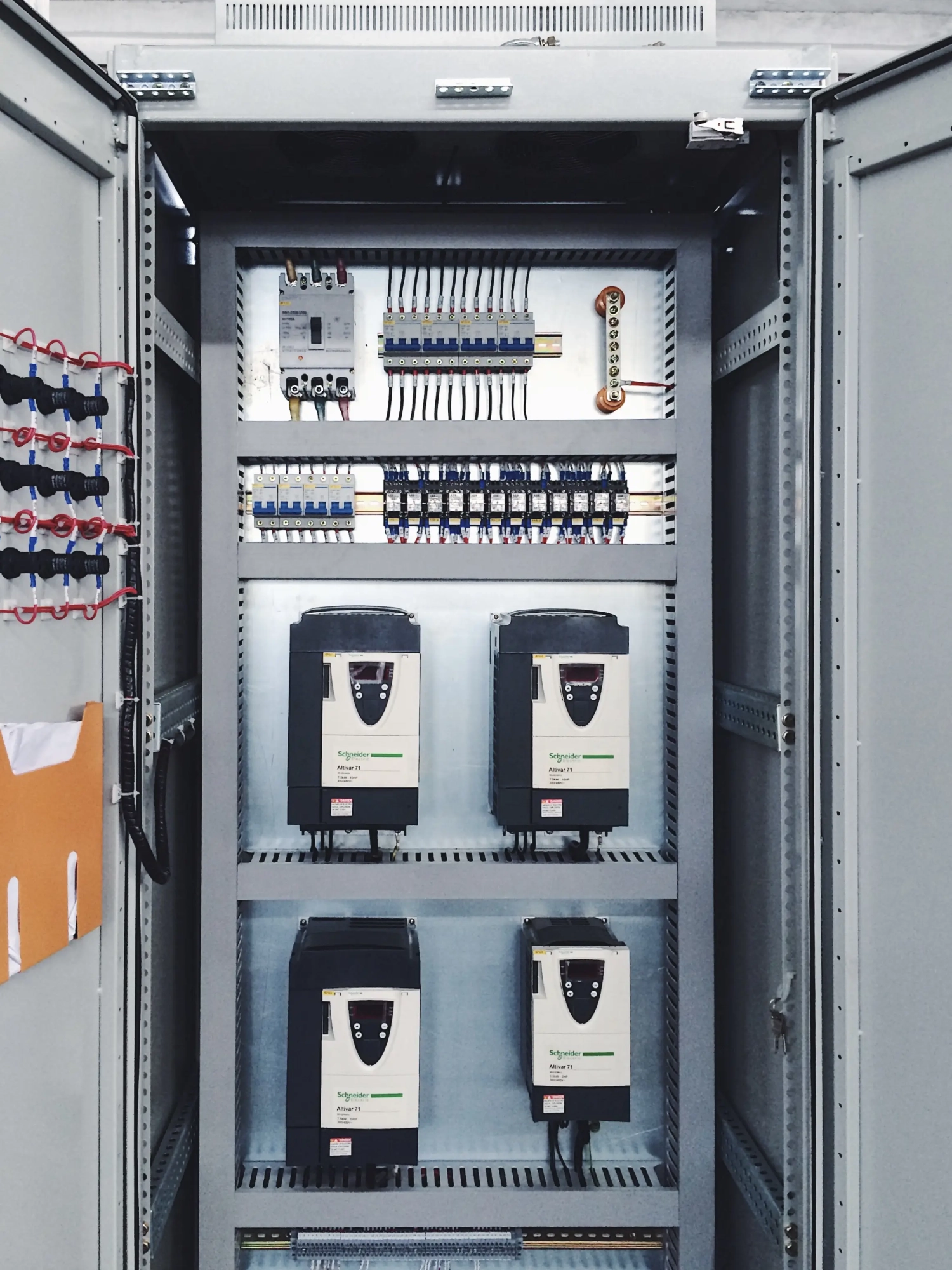
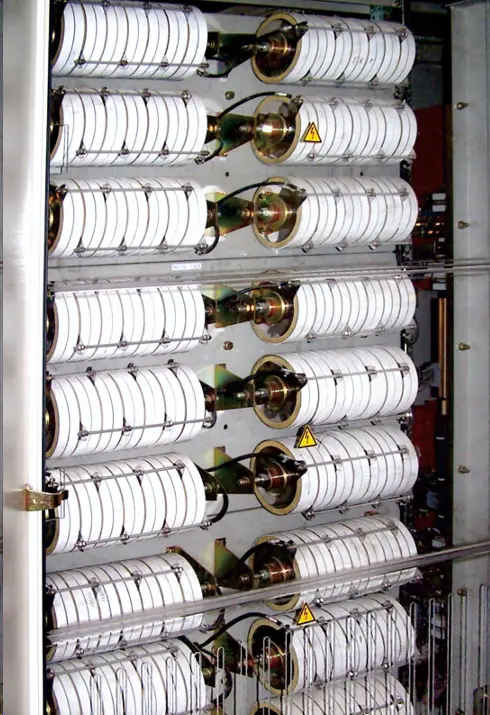
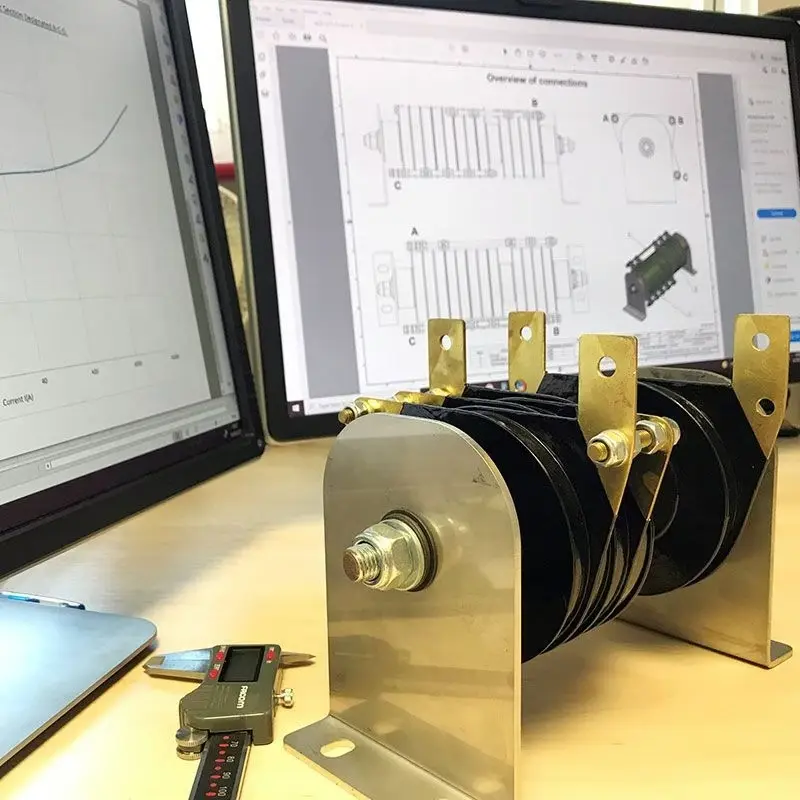
Composite demagnetization component of silicon carbide and zinc oxide, referred to as smart zinc oxide resistor. Due to its relatively soft characteristics, silicon carbide resistors effectively compensate for the hard characteristics and negative resistance of zinc oxide resistors when used in series, resulting in automatic current sharing in the parallel branch, significantly enhancing the safety of the component’s usage. It has been successfully applied in the demagnetization and overvoltage protection of rotor units in nuclear power, thermal power, and hydropower generating sets.
The CSYS series demagnetization and overvoltage protection devices are primarily used in the excitation systems of various medium and small synchronous generators. They provide demagnetization and transient overvoltage absorption under various fault conditions of the generator (including various short circuits on the stator side and generator over-excitation).
The CSYS series products include:
- CSYS1 Series: Shared intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistors for demagnetization and overvoltage protection.
- CSYS2 Series: Separate intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistors for demagnetization and overvoltage protection.
- CSYS3 Series: SiC demagnetization resistors for demagnetization and intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistors for overvoltage protection.
- CSYS4 Series: Shared SiC demagnetization resistors for demagnetization and overvoltage protection.
CSYS1 Series: Shared intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistors for demagnetization and overvoltage protection.
The intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistor completely replaces the traditional ZnO demagnetization resistor, eliminating the need for series fast fuses and enabling automatic current sharing, significantly enhancing safety and reliability. The demagnetization and overvoltage protection share a set of intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistors, which not only reduces costs but also saves space.
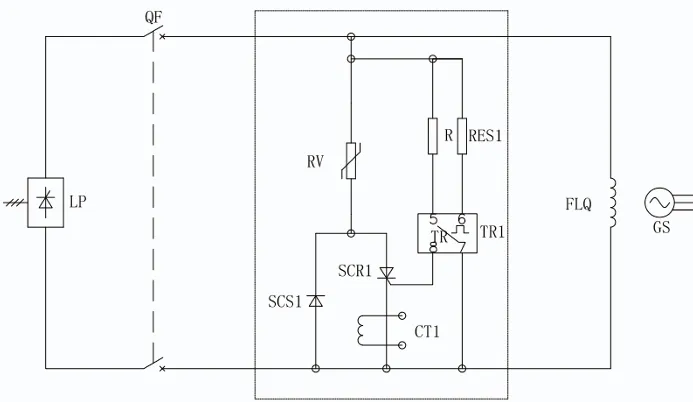
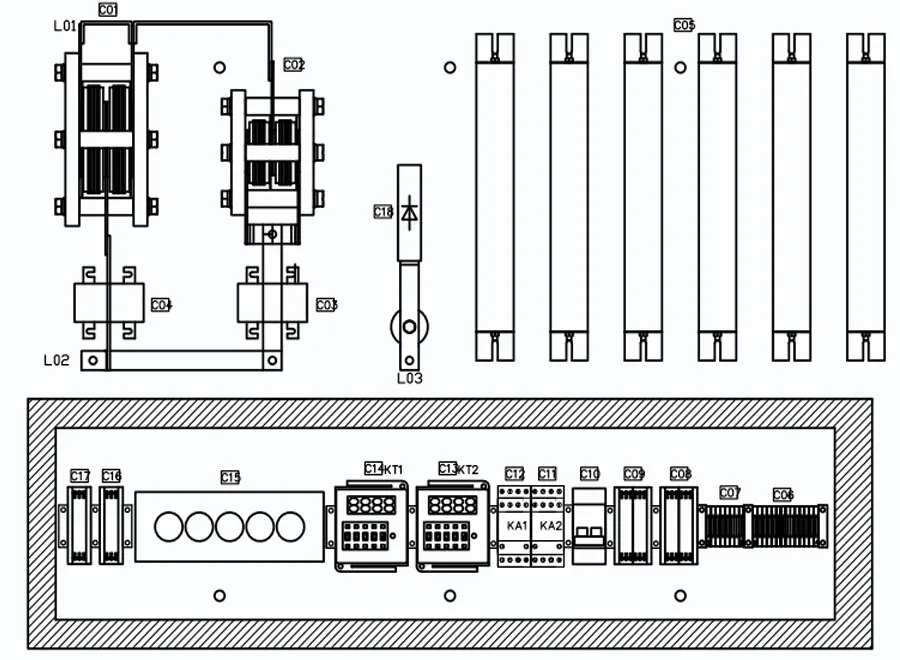
Working Principle
As shown in the diagram, the RV nonlinear resistor is used for both demagnetization and overvoltage protection. During normal operation, the QF switch is closed, and the demagnetization resistor is connected in parallel with the excitation winding. When the excitation voltage is below the threshold voltage of the demagnetization resistor, the resistor does not operate. During demagnetization, the magnetic field circuit breaker MK trips, activating the demagnetization resistor to absorb the magnetic field energy.
When the voltage across the rotor exceeds the set value, the trigger TR1 operates, turning on the thyristor, which allows the demagnetization resistor to absorb the excess energy. At the same time, the current transformer CT detects the overvoltage signal, and the counter outputs a count.
As can be seen from the diagram, by adding SCS1 and SCR1, the RV nonlinear resistor is turned off under normal operating conditions, limiting the leakage current. The selection of R and RES1 is determined based on the calculations of the overvoltage set value.
The parameters of the following components are as follows: maximum demagnetization voltage: 1000V, maximum demagnetization current: 1800A, demagnetization capacity: 0.5MJ, overvoltage trigger voltage: 1800V.
CSYS2 Series: Separate intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistors for demagnetization and overvoltage protection.
By using intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistors for both demagnetization and overvoltage protection, the advantages of traditional ZnO fast demagnetization are retained. Additionally, the intelligent zinc oxide resistors incorporate silicon carbide, which enhances safety and reliability while reducing installation space.
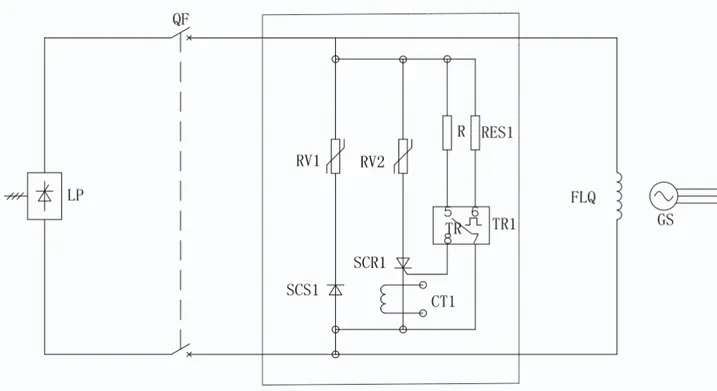
Working Principle
As shown in the diagram, the demagnetization uses the RV1 nonlinear ZnO resistor, while the overvoltage protection uses the RV2 nonlinear ZnO resistor. During normal operation, the QF switch is closed, and the demagnetization resistor is connected in parallel with the excitation winding. When the excitation voltage is below the threshold voltage of the demagnetization resistor, the resistor does not operate. During demagnetization, the magnetic field circuit breaker QF trips, activating the demagnetization resistor to absorb the magnetic field energy.
Additionally, when the voltage across the rotor exceeds the set value, the trigger TR1 operates, turning on the thyristor SCR1, which allows the RV2 nonlinear resistor to absorb the excess energy. At the same time, the current transformer CT1 detects the overvoltage signal, and the counter outputs a count.
As can be seen from the diagram, by adding SCS1 and SCR1, the nonlinear resistor is turned off under normal operating conditions, limiting the leakage current. The selection of R and RES1 is determined based on the design calculations of the overvoltage set value.
CSYS3 Series: SiC demagnetization resistors for demagnetization and intelligent ZnO demagnetization resistors for overvoltage protection.
The plan incorporates both a highly reliable silicon carbide nonlinear resistor for arc suppression and an intelligent ZnO nonlinear resistor for overvoltage absorption, achieving optimal coordination between the two.
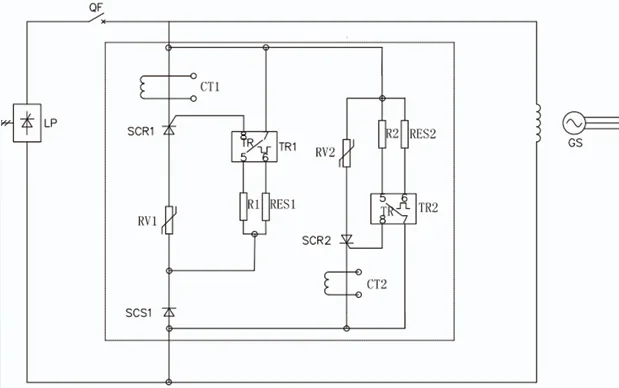
Working Principle
The RV1 silicon carbide nonlinear resistor is used for demagnetization, while the RV2 intelligent ZnO nonlinear resistor is used for overvoltage protection. During normal operation, the circuit breaker QF is closed, and SCR1 is in the off state, meaning RV1 is not in operation.
When demagnetization occurs, the magnetic field circuit breaker QF trips, triggering the TR1, which turns on the thyristor SCR1, allowing RV1 to perform demagnetization.
Additionally, when the voltage across the rotor exceeds the set value, the trigger TR2 activates, turning on the thyristor SCR2, which allows the RV2 nonlinear resistor to absorb the overvoltage. At the same time, the current transformer CT2 detects the overvoltage signal, and the counter outputs a count.
As can be seen from the diagram, by adding SCS1, SCR1, and SCR2, the nonlinear resistor is turned off under normal operating conditions, limiting the leakage current.
CSYS4 Series: Shared SiC demagnetization resistors for demagnetization and overvoltage protection.
Due to the relatively soft volt-ampere characteristics of silicon carbide nonlinear resistors, they can automatically equalize current during demagnetization and overvoltage protection. The system fully utilizes silicon carbide, significantly enhancing the safety and reliability of the system.
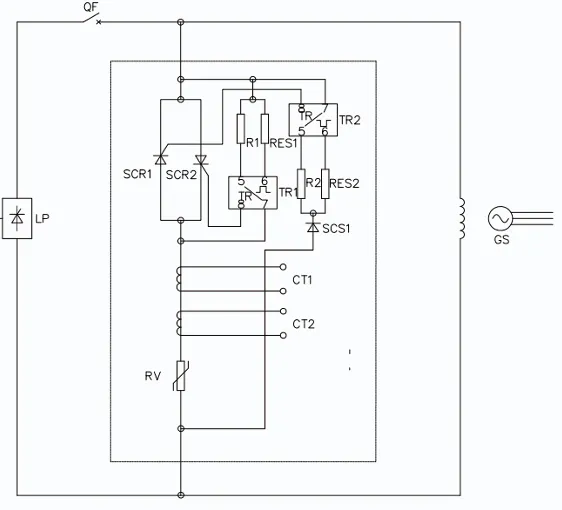
Working Principle
The RV silicon carbide nonlinear resistor is used in a circuit for both demagnetization and overvoltage protection. During normal operation, the circuit breaker QF is closed, and SCR1 and SCR2 are in the off state, meaning RV is not in operation.
When demagnetization occurs, the magnetic field circuit breaker QF trips, triggering TR2, which turns on the thyristor SCR1, allowing RV to perform demagnetization.
During normal operation, when the overvoltage exceeds the set value, the trigger TR1 activates, turning on the thyristor SCR2, which allows the RV to absorb the overvoltage. As the thyristor rectified voltage crosses zero, SCR2 turns off. At the same time, the current transformer CT1 detects the overvoltage signal, and the counter outputs a count.
The parameters of the following components are as follows: maximum demagnetization voltage: 1000V, maximum demagnetization current: 6400A, demagnetization capacity: 2MJ, overvoltage trigger voltage: 2800V.