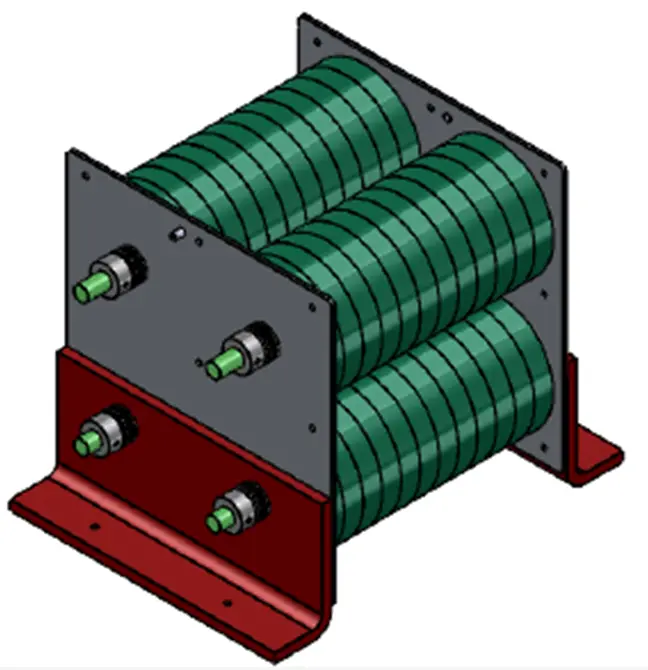
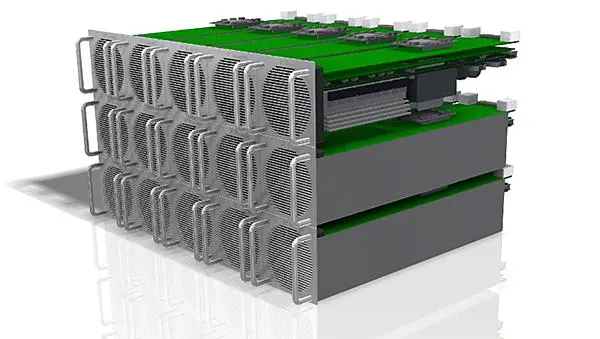
Carbon Ceramic Composite Resistors
Carbon Ceramic Composite Resistors
In the rapidly evolving semiconductor manufacturing industry, precision, speed, and thermal stability are non-negotiable. One of the critical processes in this field is dry photoresist stripping , a plasma-based technique used to remove resist materials after photolithography. This process demands components that can withstand high temperatures, rapid thermal cycling, and significant energy absorption—making the carbon ceramic composite resistor an ideal choice.
Why Carbon Ceramic Composite Resistors?
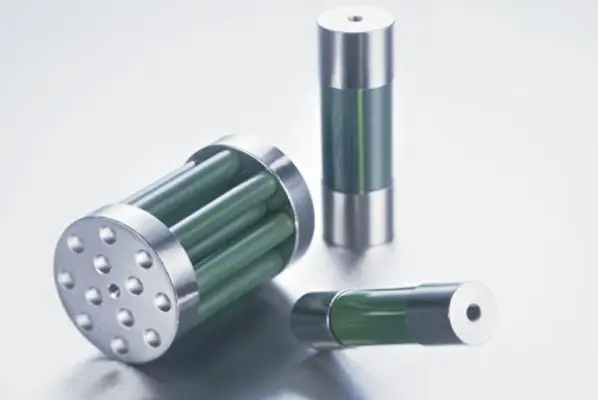
The carbon ceramic composite resistor combines the best properties of both carbon and ceramic materials. It offers excellent thermal conductivity, low thermal expansion, and superior resistance to thermal shock. These characteristics make it especially suitable for high-temperature environments like those found in semiconductor dry etching and cleaning systems.
Unlike traditional resistive elements, carbon ceramic composites maintain stable electrical performance even under extreme conditions. Their ability to absorb and dissipate large amounts of energy without degradation positions them as top-tier energy absorption resistors in modern semiconductor equipment.
Role in Dry Photoresist Stripping
During the dry photoresist stripping process, reactive gases such as oxygen or fluorine-based plasmas are used to break down and remove residual photoresist from silicon wafers. The equipment used—such as plasma etchers and ashers—requires precise temperature control and robust power management systems.
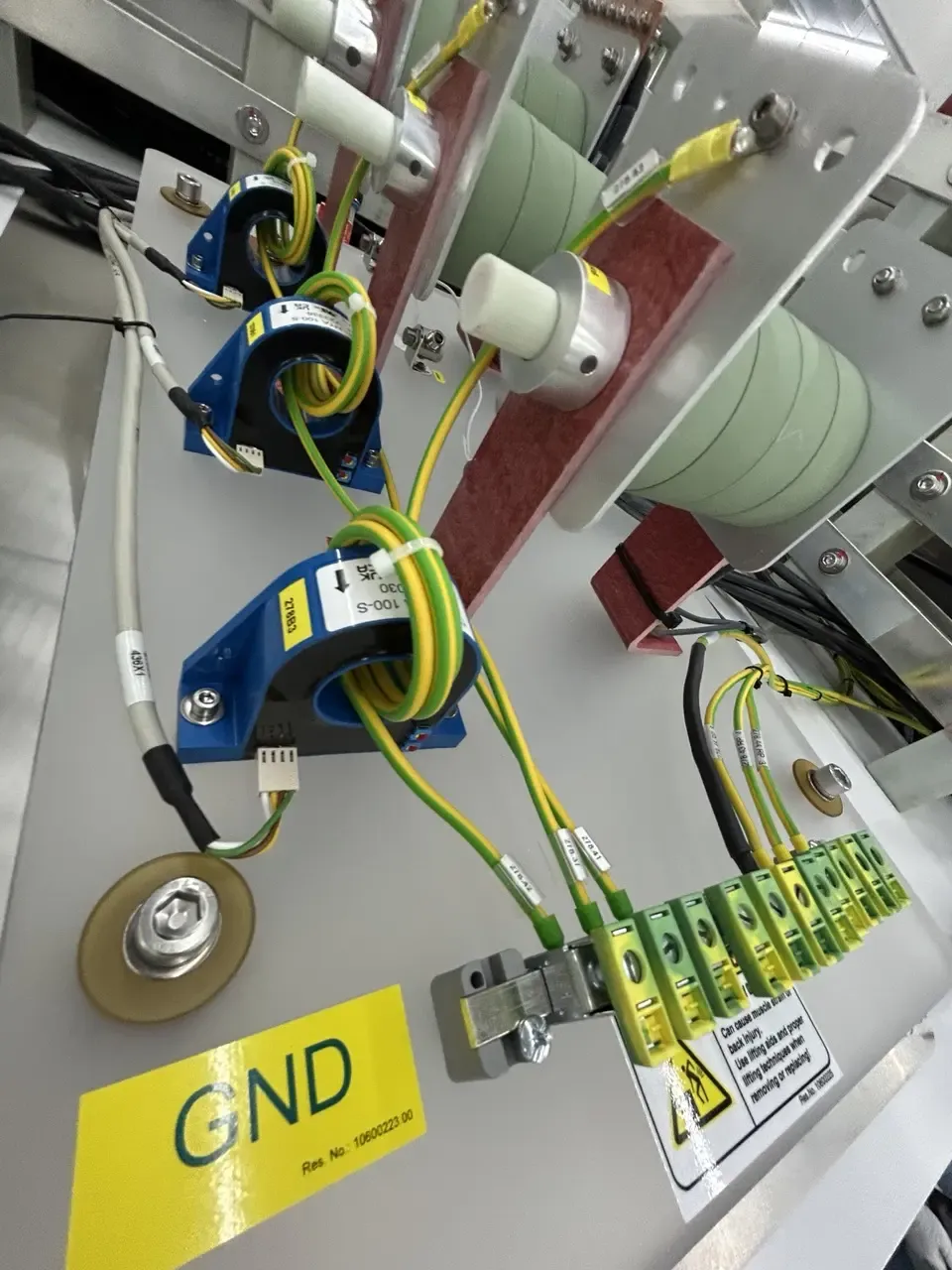
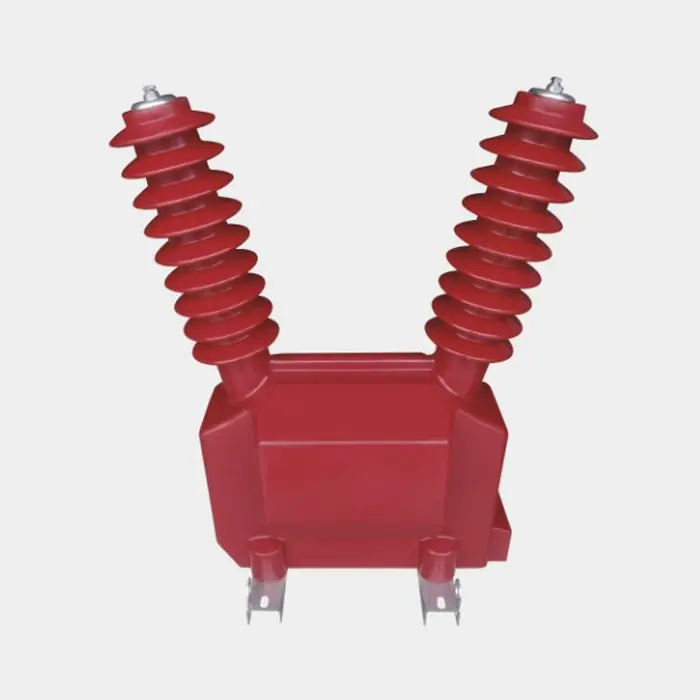
This is where disc resistors come into play. Designed with a compact, circular form factor, disc resistors made from carbon ceramic composites offer high surface area-to-volume ratios, enabling efficient heat dissipation. They are often integrated into the RF power supply circuits and bias voltage regulation modules of plasma chambers.
These energy absorption resistors help manage transient surges caused by plasma ignition and fluctuations in gas flow, protecting sensitive electronics and ensuring consistent process results. Their high durability and long operational life significantly reduce maintenance intervals and downtime in semiconductor fabrication lines.
Advantages Over Traditional Materials
Conventional resistors using metal alloys or standard ceramics may suffer from oxidation, drift, or failure under repetitive high-energy pulses. In contrast, carbon ceramic composite resistors retain their structural integrity and resistive values over time, even when exposed to aggressive chemical environments and elevated temperatures.
Moreover, their non-inductive design makes them suitable for high-frequency applications, which are increasingly common in advanced semiconductor processing tools. Whether used in RF matching networks or pulse discharge circuits, these resistors provide reliable performance and contribute to the overall efficiency and yield of the manufacturing process.
Conclusion
As semiconductor devices become smaller and more complex, the demand for high-performance, durable, and thermally stable components continues to rise. The carbon ceramic composite resistor , particularly in the form of a disc resistor , stands out as a key enabler of next-generation fabrication technologies. Its role as an energy absorption resistor in dry photoresist stripping equipment ensures safe, stable, and efficient operation—helping manufacturers meet the ever-increasing demands of the global electronics market.