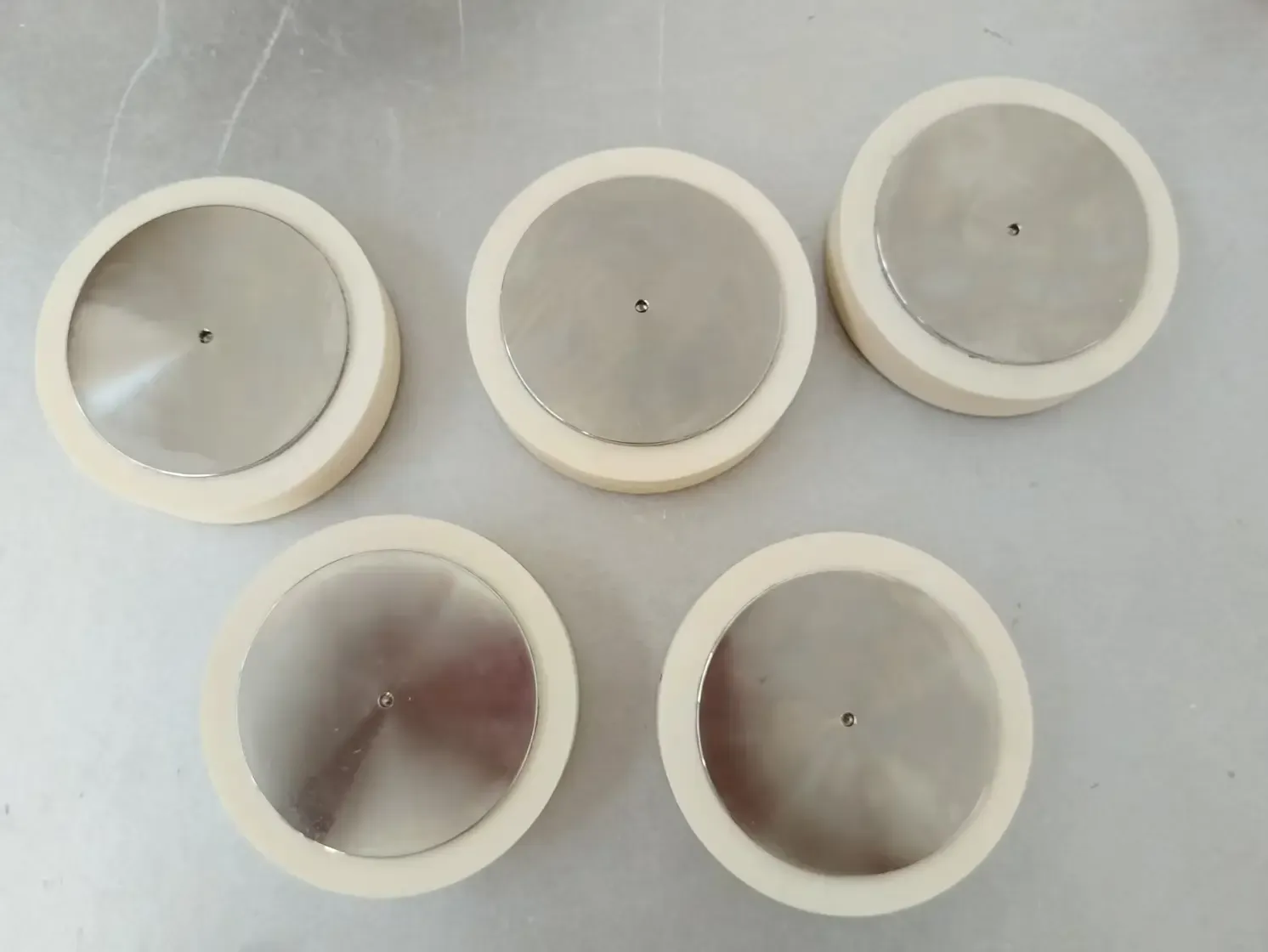
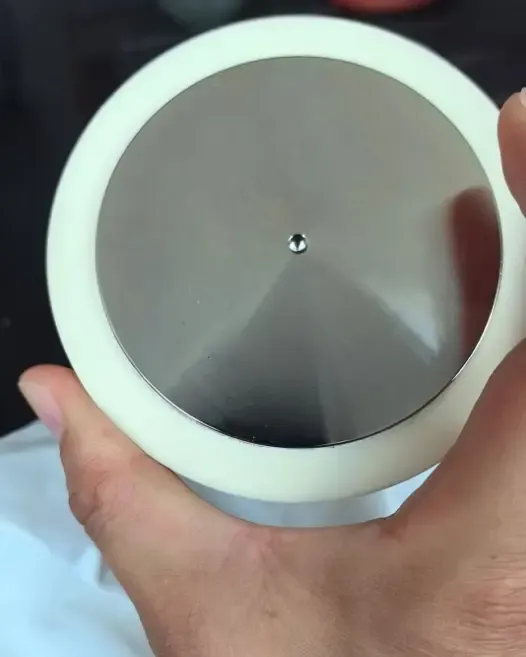
Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors
Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors
High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission systems are essential for efficient long-distance power transfer, especially in integrating renewable energy sources, interconnecting grids, and reducing transmission losses. As these systems operate under high voltage and power conditions, they face unique challenges related to transient overvoltages, switching surges, and fault conditions. To address these challenges, advanced resistor technologies, such as High-Frequency High-Power Resistors, particularly Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors, are increasingly employed to enhance system reliability, safety, and performance.
The Need for High-Frequency High-Power Resistors in HVDC
In HVDC systems, transient phenomena like lightning surges, switching operations, and fault conditions generate rapid, high-energy pulses that must be safely dissipated to prevent equipment damage. Traditional resistors may not respond quickly enough or handle the high-frequency components of these transients effectively. This is where specialized resistors designed for high-frequency, high-power applications come into play.
What Are Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors?
Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors are a class of resistors characterized by their robust construction, high thermal capacity, and excellent high-frequency response. They consist of multiple resistor elements stacked and compressed within a press pack configuration, which provides:
- Enhanced Power Handling: Capable of dissipating several kilowatts of power continuously or in pulses.
- Superior Thermal Management: The press pack design ensures uniform heat distribution and rapid heat dissipation.
- High-Frequency Response: Designed to handle transient signals with minimal inductance and parasitic effects, making them suitable for high-frequency surge absorption.
Application in HVDC Systems
1. Overvoltage and Surge Protection
Press pack ultra high power resistors are used at converter stations and line terminals to absorb switching surges and lightning-induced transients. Their high-frequency response capability allows them to effectively dissipate energy from fast-rising pulses, protecting sensitive components such as valves and insulators.
2. Filtering and Damping
In HVDC systems, these resistors serve as damping elements in filters and snubbers, reducing oscillations and stability issues caused by switching operations. Their ability to operate efficiently at high frequencies ensures system stability.
3. Fault Energy Dissipation
During faults, rapid energy release occurs. Press pack resistors can absorb and dissipate this energy quickly, preventing damage and facilitating system recovery. Their construction allows for repeated pulse handling without degradation.
Case Study: HVDC Link with Lightning Surge Absorption
In a recent HVDC project connecting offshore wind farms to the mainland grid, press pack ultra high power resistors were installed at the converter station. During a lightning storm, the resistors absorbed transient energies exceeding 100 kJ with high-frequency components, preventing damage to the converter valves. Their quick response and high power capacity ensured continuous operation and minimized downtime.
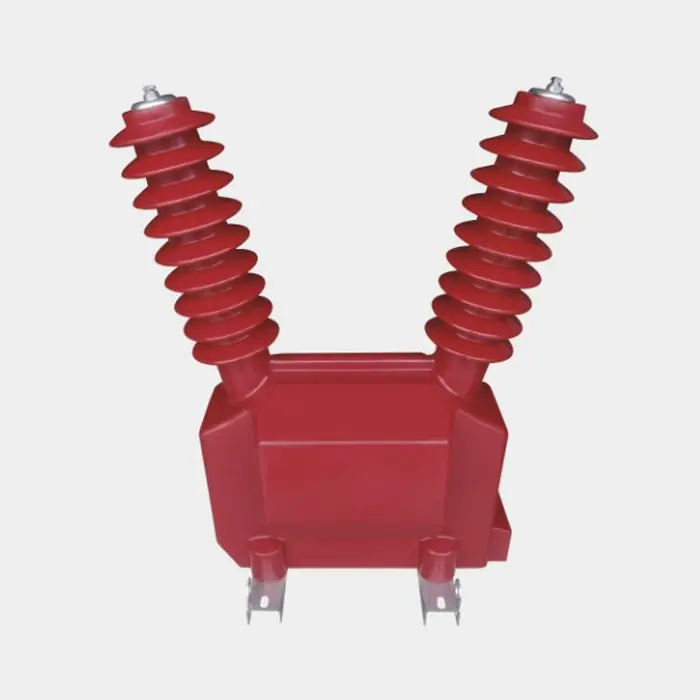
 Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors
Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors
Advantages of Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors in HVDC
- High Power Density: Can handle large energy pulses in compact sizes.
- Fast Transient Response: Suitable for high-frequency surge absorption.
- Durability and Reliability: Designed for harsh environments with long service life.
- Customizable Ratings: Can be tailored to specific system requirements.
Conclusion
Press Pack Ultra High Power Resistors are a vital component in modern HVDC transmission systems, providing effective high-frequency, high-power surge absorption. Their advanced design and performance capabilities significantly enhance the resilience and stability of HVDC networks, ensuring reliable long-distance power delivery in the face of transient disturbances.
Specifications
| Parameter | DISC100 | DISC130 | DISC150 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance Range | 320mΩ~1Ω (Other values available upon request) | 320mΩ~1Ω (Other values available upon request) | 320mΩ~1Ω (Other values available upon request) |
| Resistance Tolerance | ±5%~±10% | ±5%~±10% | ±5%~±10% |
| Maximum Working Voltage | 1kV DC | 1kV DC | 1kV DC |
| Peak Voltage Rating | 3kV DC | 3kV DC | 3kV DC |
| Cut-off Temperature (Chip) | 220°C | 220°C | 220°C |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +150°C | -40°C to +150°C | -40°C to +150°C |
| Creepage Distance | 41.7mm | 41.7mm | 41.7mm |
| Electrode Flatness | ≤0.05mm | ≤0.05mm | ≤0.05mm |
| Electrode Parallelism | ≤0.05mm | ≤0.05mm | ≤0.05mm |
| Parasitic Inductance | ≤0.5μH, 10kHz | ≤0.5μH, 10kHz | ≤0.5μH, 10kHz |
| Mounting Method | Double-sided mounting, water-cooled heat dissipation | Double-sided mounting, water-cooled heat dissipation | Double-sided mounting, water-cooled heat dissipation |
| Rated Power | 3kW, Base plate temperature ≤25°C | 5kW, Base plate temperature ≤85°C | 6kW, Base plate temperature ≤85°C |
| Short-time Overload | 6kW-10s, Base plate temperature ≤25°C | 10kW-10s, Base plate temperature ≤85°C | 12kW-10s, Base plate temperature ≤85°C |
| Maximum Single Pulse Energy | 1000J, RC discharge time constant ≥250μs | 2000J, RC discharge time constant ≥250μs | 2500J, RC discharge time constant ≥250μs |
| Steady-state Thermal Resistance (Unidirectional) | 0.12K/W | 0.10K/W | 0.05K/W |
| Pressure Force | 40-70kN | 60-100kN | 60-100kN |
This table summarizes the specifications for the DISC100, DISC130, and DISC150 devices, including their resistance ranges, voltage ratings, temperature limits, mechanical dimensions, electrical characteristics, and thermal performance.