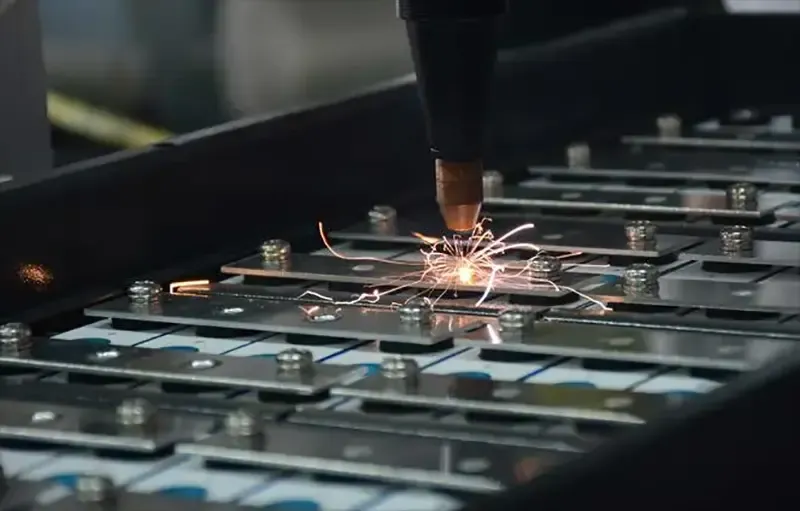
1. Application Background A battery manufacturing company for new energy vehicles needs to develop a high-precision battery module welding machine. The requirements include stable and controllable welding current, high heat dissipation efficiency, and the ability to adapt to different specifications of battery tabs (thickness of 0.5~2mm). After technical evaluation, a 5kW water-cooled resistor was selected as the core heating element, enabling different welding power outputs by switching between 10Ω and 20Ω resistance values.
2. Design Requirements Analysis 1. Power Requirements Welding power range: 2kW5kW (for thin/thick tab welding) Voltage range: DC 100V200V (dynamically matched according to resistance value) 2. Cooling Requirements The temperature rise of the resistor surface under continuous operation must be ≤40℃ Cooling water flow rate ≥8L/min, inlet water temperature ≤25℃ 3. Resistance Switching Logic 10Ω resistor: for high current mode (I=√(P/R)=√(5000/10)=22.36A) 20Ω resistor: for low current mode (I=√(5000/20)=15.81A)
3. System Design Plan 1. Resistor Selection 10Ω Water-Cooled Resistor: Structure: Stainless steel tube encapsulation, outer diameter 20mm, length 300mm Cooling Method: Dual parallel water ducts, water flow rate 4L/min per duct 20Ω Water-Cooled Resistor: Structure: Nickel-chromium alloy wire wound type, ceramic substrate insulation Cooling Method: Single spiral water duct, water flow rate 8L/min
2. Control Circuit Design Power Switching Module: Controlled by PLC to switch the relay group for connecting the 10Ω/20Ω resistors into the circuit, achieving power level adjustment. Protection Mechanism: Water flow sensor linkage: Automatically reduce power to 2kW if flow is insufficient Temperature feedback: NTC probe monitors the resistor temperature in real-time, with over-temperature alarm
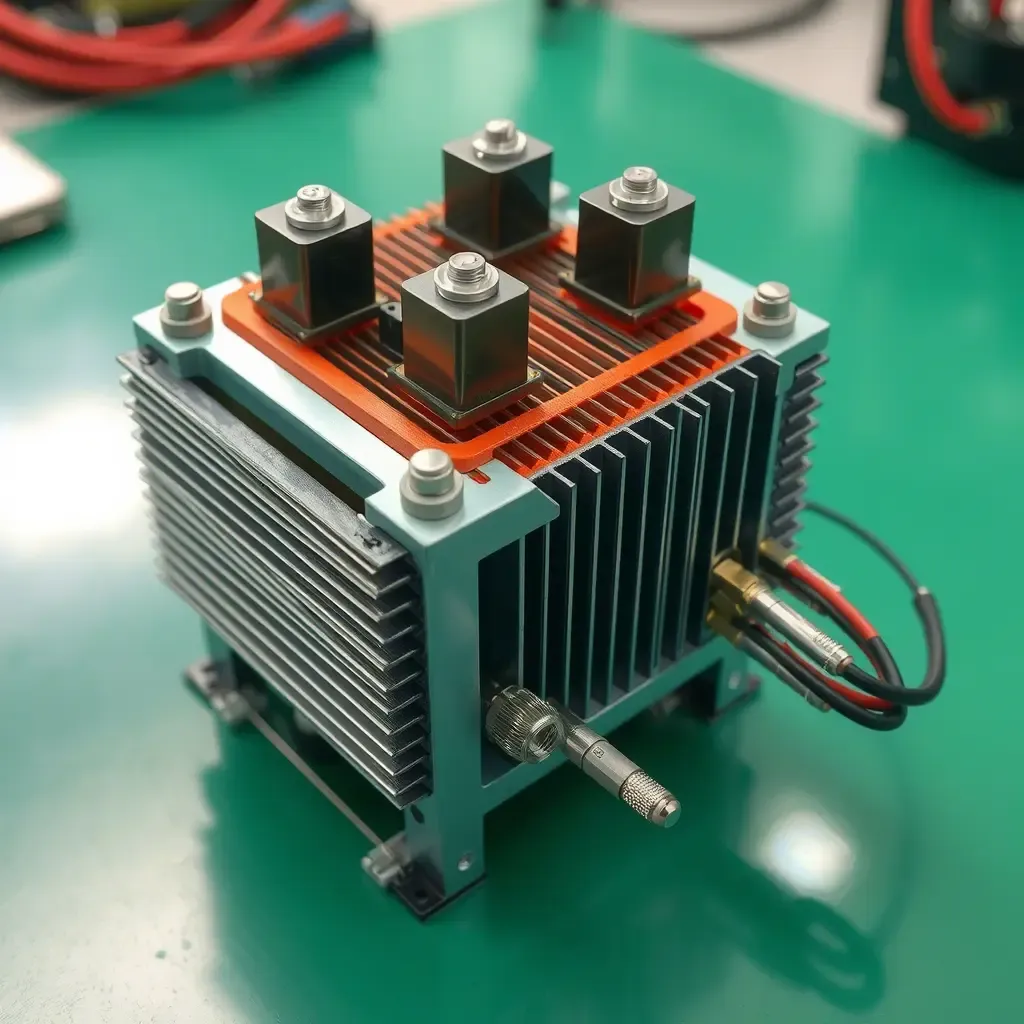
3. Welding Process Validation | Parameter | 10Ω Mode (Thick Tabs) | 20Ω Mode (Thin Tabs) | |—————-|————————|—————————| | Welding Current (A) | 22.36 | 15.81 | | Welding Time (ms) | 200500 | 100300 | | Weld Shear Strength (N)| ≥2000 | ≥1200 | | Resistor Temperature Rise (℃)| 35 | 28 |
4. Implementation Results 1. Increased Production Efficiency: The dual resistance switching function reduces equipment downtime for switching types, increasing the production line pace from 12ppm to 18ppm. 2. Energy Consumption Optimization: Energy consumption is reduced by 30% when welding thin tabs in the 20Ω mode, resulting in an annual savings of approximately 120,000 yuan in electricity costs. 3. Reliability Validation: Continuous operation for 1000 hours without failure, with a resistance drift of less than 1% (measured ΔR=0.08Ω at 10Ω setting).
5. Technical Summary Resistance Selection Logic: 10Ω is suitable for high heat demand scenarios (e.g., welding dissimilar metals such as copper and aluminum), while 20Ω is used for precision temperature control scenarios (e.g., welding thin foil materials). Water Cooling System Optimization: It is recommended to use a deionized water and ethylene glycol mixture (proportion 6:4) as the cooling medium to prevent scaling and corrosion. Expanded Applications: The continuous adjustable resistance can be achieved through PWM voltage adjustment technology, further adapting to gradient welding needs.
Appendix: Resistor Power Calculation Formula** \[ P = I^2R = \frac{V^2}{R} \] (Note: In practical applications, contact resistance and electrode voltage drop effects should be considered, and a power reserve of 20% is recommended.)