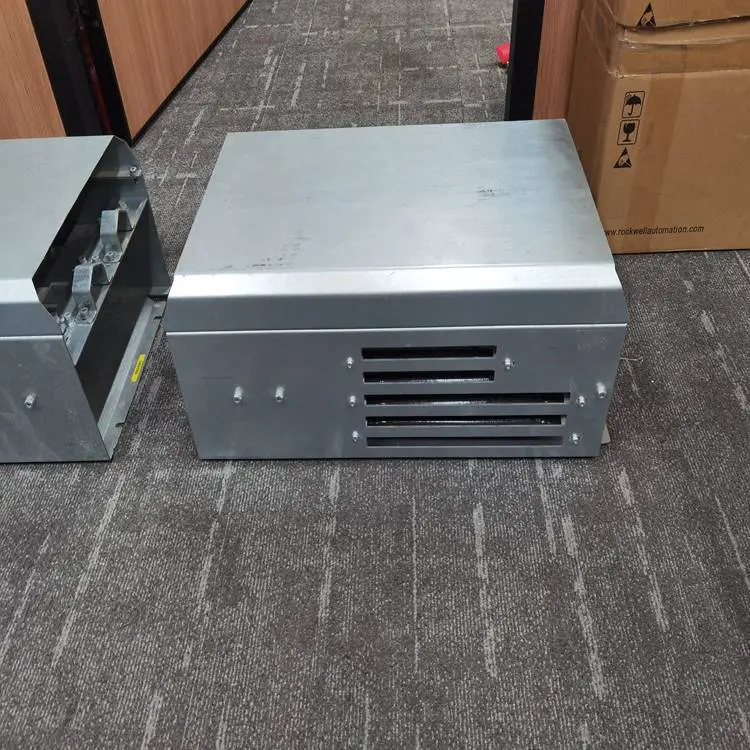
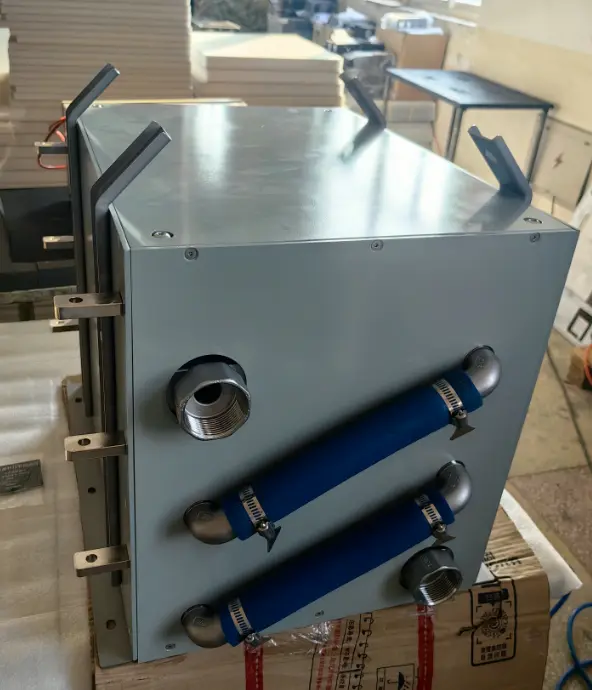
A braking chopper is a device used in power conversion systems to control and regulate excess energy generated during the braking process of motors or generators. Its primary function is to convert surplus energy into heat or feed it back into the power grid, thereby enabling energy absorption and transfer. Braking choppers are widely applied in industries such as industrial automation, transportation, wind power generation, and electric vehicles, significantly improving system efficiency, safety, and reliability.
Working Principle of Braking Choppers
Braking choppers utilize different operational methods to consume and convert excess energy based on the amount generated during motor or generator braking.
1.1 DC Braking Chopper: Suitable for DC motors or equipment powered by DC sources. During braking, the chopper dissipates excess energy by connecting to external resistors or feeding energy back into the grid. This prevents system overloads and energy losses, protecting associated equipment.
1.2 AC Braking Chopper: Designed for AC motors or equipment operating on AC power. During braking, it absorbs and transfers energy by connecting to external resistors, capacitors, or by returning energy to the grid. This enhances system stability and reduces dependence on external power sources.
Features of Braking Choppers
Braking choppers possess a range of unique characteristics and advantages, making them an essential component in power conversion systems.
2.1 Energy Regeneration: Braking choppers can return excess energy generated during braking back to the grid, enabling energy reuse, improving system efficiency, and reducing energy waste and environmental pollution.
2.2 Overload Protection: They effectively protect motors and other equipment from overload damage by dissipating or transferring excess braking energy, ensuring system safety and reliability.
2.3 Space-Saving Design: With a compact design that occupies minimal space, braking choppers are suitable for various industrial equipment and power systems, especially in space-constrained environments.
2.4 Fast Response: Equipped with rapid response capabilities, braking choppers quickly absorb and transfer braking energy, ensuring stable system operation and preventing negative effects caused by energy accumulation.
Functions of Braking Choppers
Braking choppers play a critical role in power conversion systems, offering the following key functions:
3.1 Energy Dissipation: By connecting to external resistors or feeding energy back into the grid, braking choppers dissipate excess energy generated during braking, preventing system overloads and energy losses.
3.2 System Stability: They effectively manage surplus energy produced during motor braking, enhancing system stability, preventing oscillations or loss of control, and ensuring smooth motor operation.
3.3 Overload Protection: They prevent motor damage caused by overloads during braking by absorbing and redirecting excess energy, thereby protecting motors and other components from adverse effects.
3.4 Energy Utilization: By feeding surplus energy back into the grid, braking choppers enable energy reuse, reduce operating costs, and improve energy efficiency—especially beneficial in renewable energy systems.
3.5 Environmental Friendliness: The energy regeneration and dissipation capabilities of braking choppers make them an eco-friendly solution, reducing reliance on conventional energy sources and lowering carbon emissions and environmental impact.
In summary, braking choppers play an indispensable role in power conversion systems. Through their unique operating principles and features, they provide reliable energy management solutions across various industries. As industrial technology continues to advance, braking choppers will see increasingly widespread application and contribute significantly to the sustainable development of power conversion systems.