Concepts of High-Voltage Resistances and Pulse Resistances High-voltage resistors are resistors that can operate in a continuous high-voltage environment. Pulse resistors are those that can withstand momentarily high voltage. When continuous high working voltage is required, designers need to select high-voltage resistors, which typically have large or very large resistance values, generally above 1K ohms, with maximum values exceeding 100T (10 raised to the power of 14 ohms) and working resistances ranging from several thousand volts to several hundred thousand volts or even higher. In normal operating conditions with low working voltage, but capable of withstanding very high momentary pulses or very large instantaneous energy, pulse resistors, also known as high-energy resistors, are needed. High-energy resistors typically have resistance values much smaller than high-voltage resistors; the smaller the resistance, the faster the energy release, requiring higher pulse withstand characteristics for the resistor itself. Pulse resistors of the same material and power generally share common pulse withstand characteristics, but the level of resistance will affect their pulse endurance capability.
Applications of High-Voltage Resistors and Pulse Resistors High-voltage resistors are used in a wide range of applications, such as high-voltage electrical equipment, medical CT and X-ray machines, high-voltage testing equipment, high-voltage power supplies, vacuum equipment, and so forth. Pulse resistors are commonly used in automotive electronics, cardiac defibrillators, and other medical devices, as well as in high-voltage power supplies. In power designs where arcing may occur, pulse resistors can improve system reliability.
Classification and Characteristics of High-Voltage Resistors and Pulse Resistors According to materials, high-voltage resistors are classified into: glass enamel high-voltage resistors, metal oxide film high-voltage resistors, carbon composite high-voltage resistors, ceramic composite high-voltage resistors, thick film high-voltage resistors, and ruthenium oxide high-voltage resistors. Glass enamel high-voltage resistors are the most common type, characterized by low cost and typical application in low-power situations where reliability is not highly critical. Metal oxide film high-voltage resistors are often used as loads in high-frequency resistors, but their long-term stability is relatively poor, and their pulse endurance is generally average, with lower power ratings. Carbon and ceramic composite high-voltage resistors have very low inductance, excellent high-voltage performance, and pulse resistance, but their resistance value accuracy typically reaches only 5% at best, with high temperature drift and average long-term stability of resistance values. They are suitable for applications requiring high voltage and high pulse tolerance but with moderate resistance value precision. Thick film high-voltage resistors are currently the most popular on the market, generally rated below 20W, non-inductive, with resistance values exceeding 1T, and accuracy reaching 0.5% or better, with the lowest temperature drift as low as 25 PPM. Their pulse endurance is slightly lower than that of carbon and ceramic composite resistors, but they can also be customized for precise voltage dividing high-voltage resistors and high-voltage network resistors. The main drawback of ruthenium oxide high-voltage resistors is their high cost and long manufacturing cycle. However, they provide excellent temperature drift (10 PPM) and very high precision (0.05%), with a wide range of resistance values, making them suitable for precise high-voltage control applications. Pulse resistors can be classified by materials into: carbon composite pulse resistors, ceramic composite high-energy resistors, wire-wound high-energy resistors, and thick film pulse resistors.
Insights Published Mar 7, 2025 Updated Dec 1, 2025 3 min read
Keep exploring
More articles for your team
10 MAR
InsightsHigh-Voltage Thick Film Resistors Customization for Medical X-Ray & MRI Systems
Mar 10, 2025 Read more →

05 MAR
InsightsThe High Energy Carbon Ceramic Resistors Functions in Arc Extinguishing in Ultra-High Voltage Circuit Breakers; What Is The Principle Behind This?
Mar 5, 2025 Read more →
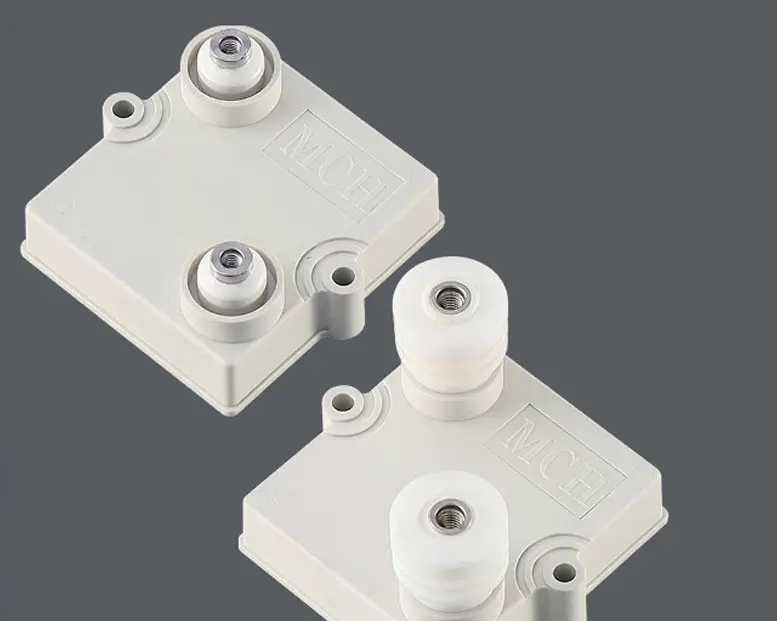

27 NOV
InsightsWhy Thick-Film Planar Power Resistors Are Quietly Becoming the First Choice for Harsh Energy Circuits
Thick-Film Planar Power Resistors
Nov 27, 2025 Read more →
27 NOV
InsightsThick-Film Chip High-Voltage Resistors: The 700-Volt-Per-Millimetre Solution Hiding in Plain Sight
High-Voltage Resistors Thick-Film Chip High-Voltage Resistors
Nov 27, 2025 Read more →