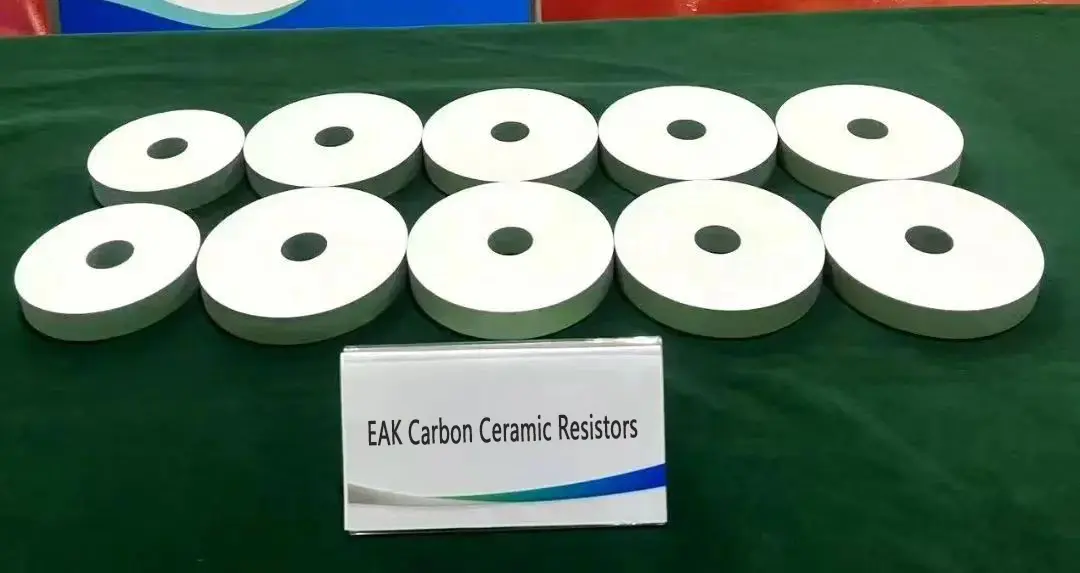
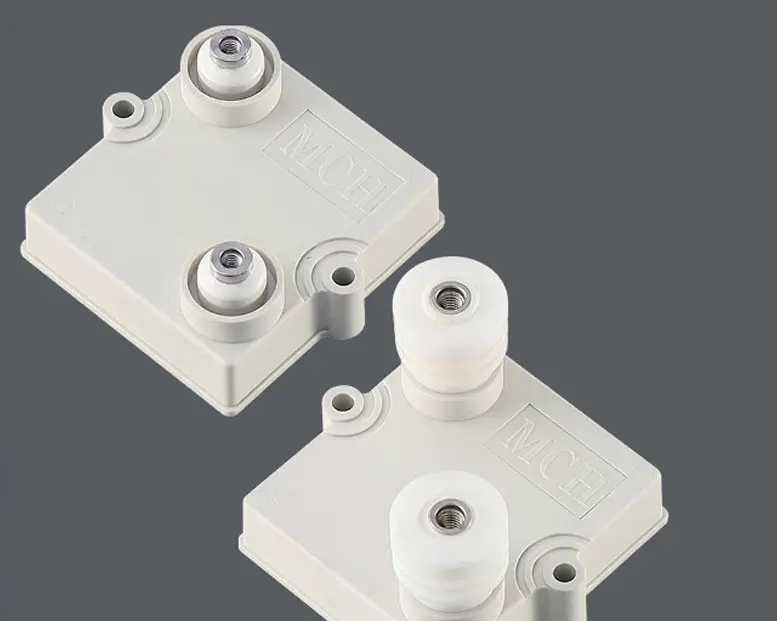
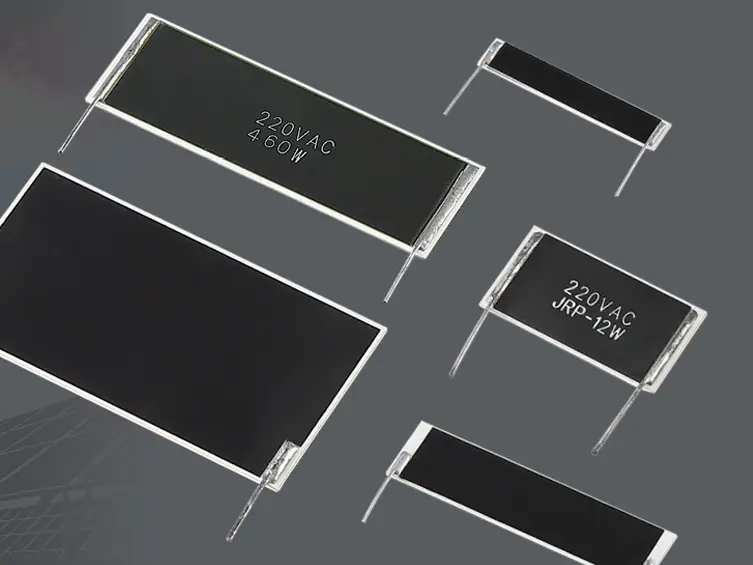
In the world of advanced electronics, the demand for high-power thick film resistors with exceptional performance is growing rapidly. These components play a critical role in applications such as power electronics, automotive systems, renewable energy solutions, and industrial equipment. One of the most promising innovations in this field is the use of carbon nanotube-based thick film resistors. With their unique properties, such as a low temperature coefficient and excellent power-handling capabilities, these resistors are redefining what is possible in electronic design.
Why Carbon Nanotube Thick Film Resistors Stand Out
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have long been celebrated for their extraordinary electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. When incorporated into thick film resistor pastes with a resistivity of 5 Ω·cm , they offer several key advantages:
- Low Temperature Coefficient Thick Film Resistors : Temperature stability is crucial for resistors used in precision applications. Carbon nanotube-based resistors exhibit an exceptionally low temperature coefficient , often in the range of 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹. This ensures minimal resistance variation over a wide temperature range, making them ideal for environments where thermal fluctuations are common. Whether in aerospace, automotive, or industrial settings, these resistors maintain consistent performance even under extreme conditions.
- High Power Handling Capability : The ability to dissipate heat efficiently is essential for high-power thick film resistors . Carbon nanotube resistors achieve this through their excellent thermal conductivity and robust structural integrity. By optimizing the design—such as increasing film thickness or using advanced substrate materials like aluminum oxide or aluminum nitride—these resistors can handle significantly higher power levels without compromising performance or reliability.
- Inductance-Free Design : In high-frequency applications, parasitic inductance can degrade performance. Carbon nanotube thick film resistors are designed with symmetric layouts and short current paths, ensuring an inductance-free operation . This makes them suitable for RF and microwave circuits, where signal integrity is paramount.
Key Design Considerations for Maximum Performance
To fully leverage the potential of carbon nanotube thick film resistors, careful attention must be paid to their design and fabrication process:
- Resistivity Optimization : The resistivity of the paste (5 Ω·cm) allows engineers to tailor the resistor’s value by adjusting parameters like film thickness and electrode spacing. For example, thicker films can reduce resistance while enhancing power dissipation capabilities.
- Thermal Management : Heat dissipation is a critical factor in ensuring long-term reliability. Using substrates with high thermal conductivity and incorporating additional cooling mechanisms (e.g., heatsinks or forced airflow) can significantly improve the resistor’s power rating.
- Precision Manufacturing : Achieving uniformity in the carbon nanotube paste deposition and sintering processes is vital to maintaining low temperature coefficients and consistent performance across batches.
Applications Across Industries
The versatility of carbon nanotube thick film resistors makes them indispensable in various industries:
- Automotive Electronics : Modern vehicles rely on sophisticated electronic control systems that require stable, high-power resistors. Carbon nanotube resistors meet these needs while operating reliably in harsh environments.
- Renewable Energy Systems : In solar inverters and wind turbine converters, high-power thick film resistors help manage large currents and voltages, contributing to system efficiency and longevity.
- Telecommunications : With their low temperature coefficient and inductance-free design, these resistors are perfect for telecommunications infrastructure, including 5G networks and satellite communications.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, the need for innovative solutions like carbon nanotube thick film resistors becomes increasingly evident. These components combine the benefits of high-power handling , low temperature coefficients , and inductance-free operation , making them a game-changer in the electronics industry. Whether you’re designing cutting-edge power electronics or precision instrumentation, carbon nanotube-based resistors provide unmatched performance and reliability.
If you’re looking for the next generation of high-power thick film resistors or low temperature coefficient thick film resistors , consider integrating carbon nanotube technology into your designs. With its unparalleled combination of properties, it’s no wonder this material is shaping the future of electronic components. Explore the possibilities today and stay ahead of the curve in your field!
By focusing on these keywords—high-power thick film resistors and low temperature coefficient thick film resistors —this article not only educates readers but also enhances search engine visibility, driving organic traffic to your content.