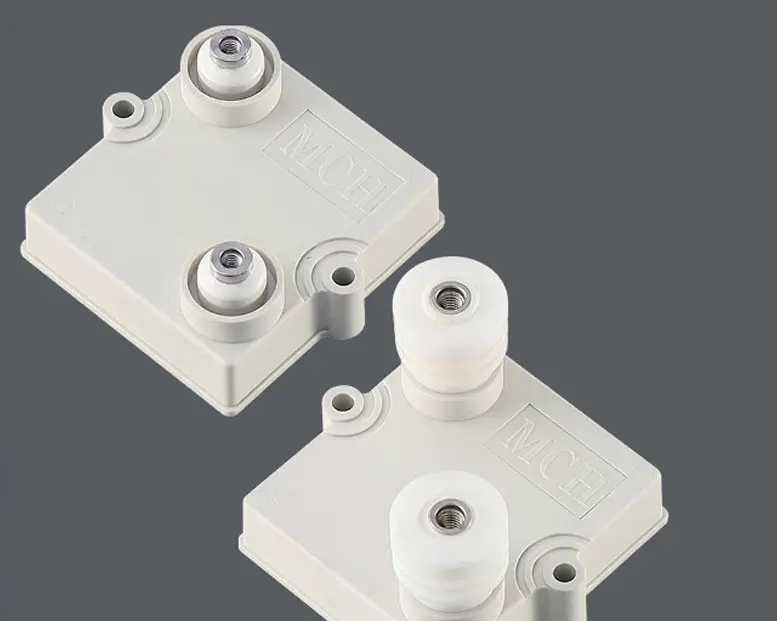
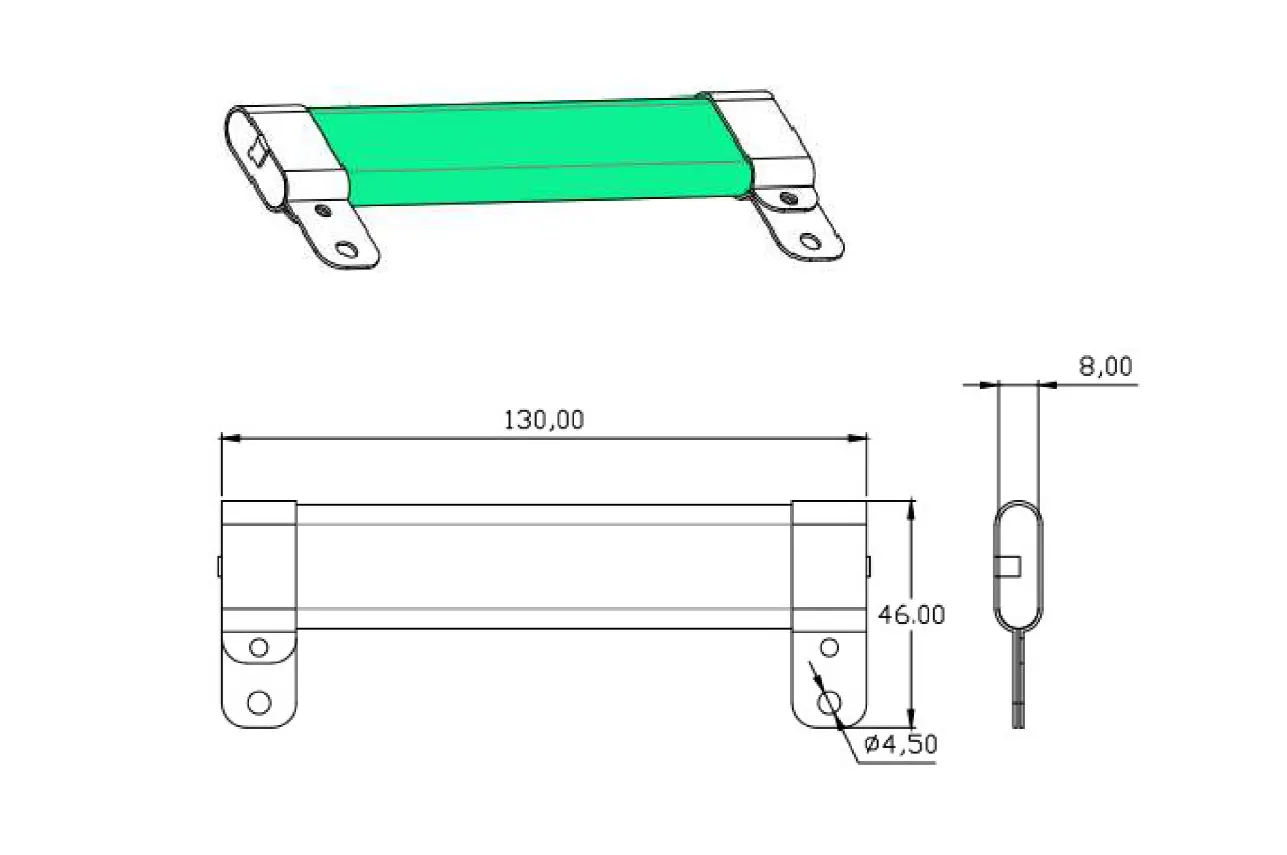
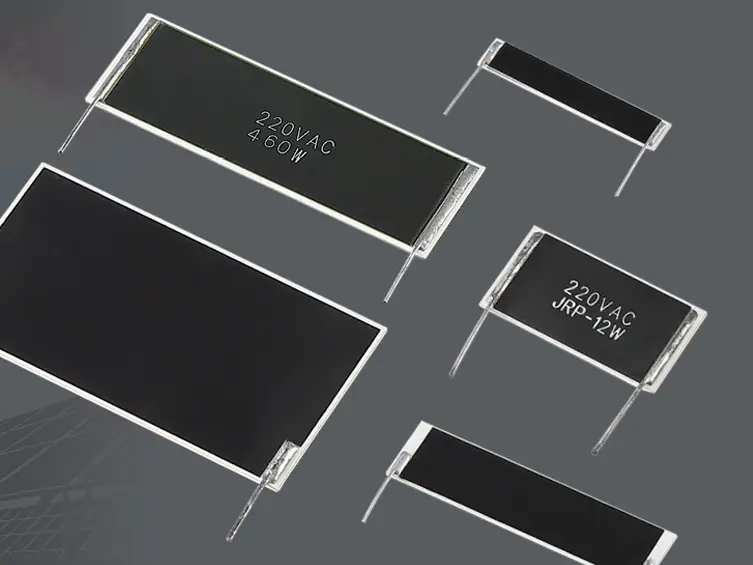
High-energy ceramic resistors are a vital component in modern electronic circuits, particularly when it comes to managing and absorbing transient energy in capacitive applications. Here’s an in-depth look at how these resistors function, their benefits, and where they are typically used.
Understanding Ceramic Resistors
Ceramic resistors are made from high-grade ceramic materials mixed with metallic oxides. This composition gives these resistors unique electrical properties:
High Thermal Stability: Ceramic materials can withstand high temperatures without degradation, making them ideal for environments where heat might be an issue.
Resistance to Overload: Unlike many other types of resistors, ceramic resistors can handle significant electrical stress, including high voltage spikes or surges.
Dielectric Properties: The ceramic body acts as an excellent insulator, which is crucial for the capacitive absorption role.
Capacitive Absorption Explained
Capacitive absorption involves the management of energy spikes, particularly those caused by the discharge of capacitors. When a capacitor discharges, it can release a burst of energy that might damage sensitive electronic components if not controlled. Here’s how ceramic resistors come into play:
Energy Dissipation: When a capacitor discharges, the high-energy ceramic resistor absorbs this energy, converting it into heat rather than allowing it to flow freely through the circuit. This helps in protecting other components from potential damage due to voltage spikes.
Time Constant Adjustment: The combination of resistance and the inherent capacitance of the circuit can adjust the time constant of the discharge. Ceramic resistors can be tailored to specific resistance values to control the rate at which energy dissipates.
Applications of High-Energy Ceramic Resistors
Power Supplies: In switch-mode power supplies, these resistors help manage the inrush current when the circuit initially powers up or when capacitors discharge during operation.
Pulse Circuits: For circuits dealing with pulses, especially where timing and signal integrity are crucial, ceramic resistors ensure that the discharge of capacitors does not introduce noise or damage.
SNUBBER Networks: Used in snubber networks to suppress voltage spikes and protect semiconductors like transistors and thyristors from high-voltage transients.
Automotive Electronics: Given their robustness, these resistors are used in automotive applications where reliability under harsh conditions (like heat, vibration, or electrical noise) is paramount.
Design Considerations
Selection of Resistance: The choice of resistance value is critical. Too high, and it might not absorb enough energy; too low, and it might not manage to dissipate the energy effectively before it affects other components.
Physical Size and Power Rating: The physical size of the resistor relates directly to its ability to absorb and dissipate energy. A larger resistor can handle more power but might not fit in tight spaces.
Frequency Response: In high-frequency applications, the parasitic capacitance of the resistor itself needs consideration to ensure it does not adversely affect circuit performance.
Conclusion
High-energy ceramic resistors play a crucial role in electronic design, especially where energy management from capacitive discharges is required. Their ability to absorb, manage, and dissipate energy safely makes them indispensable in applications demanding reliability and protection against electrical surges. As technology progresses, the development of these components continues to evolve, offering even better performance characteristics tailored to the ever-increasing demands of modern electronics.